今回は、RaspberryPiのネットワーク設定を紹介していきたいと思います。
多くの方がRaspberryPiをwifiに接続して操作すると思います。
今回、wifiだけでなく、Ethernetを使用した方法も紹介するので是非参考にしてください。
RaspberryPiのWifi設定
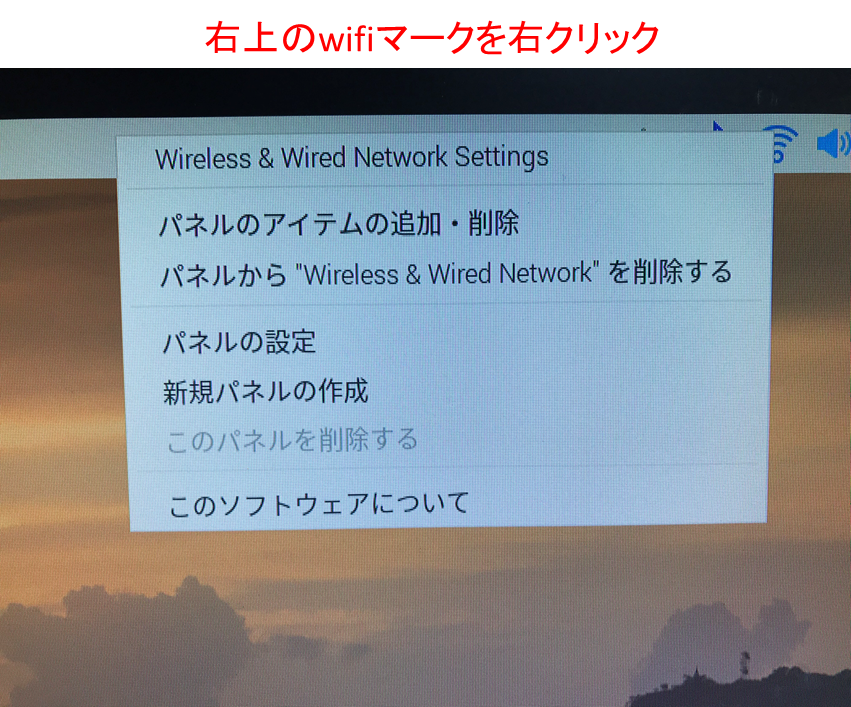
デスクトップ画面から設定する場合(GUI)
wifiの設定はほとんどセットアップ時に設定してしまうので、新規にwifiを登録したいと思った時に必要になるぐらいかと思います。
以下の画面が出てくるので、
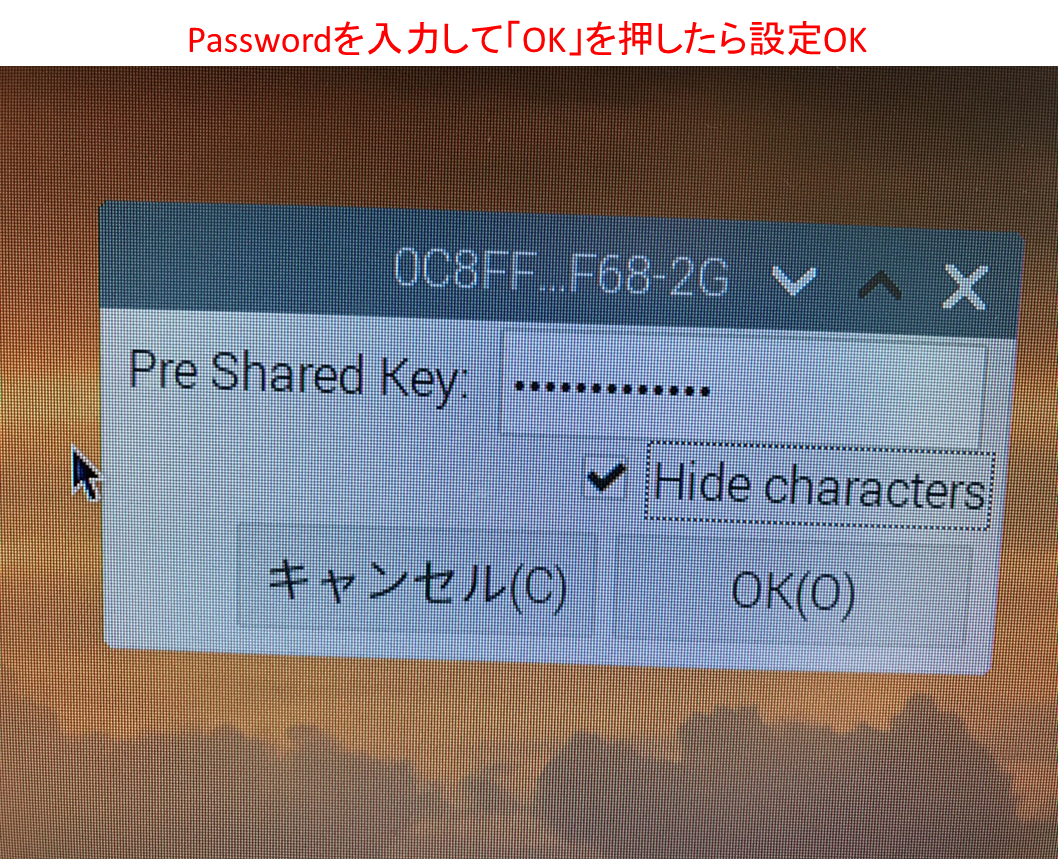
※「Automaticaly~」のチェックは外しておきましょう。
すると、パスワード入力が求められるので、パスワード入力したらOKです。
コマンドラインから設定する場合(CUI)
今度は、コマンドラインからの設定方法を紹介します。
自分は、コマンドラインからの設定の方が簡単でいいと思います。
①まずwifiスポットを検索しましょう。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo iwlist wlan0 scan | grep ESSID
ESSID:"0C8FFree-2G"
ESSID:"Freewifi1"
ESSID:"0C8F12DF87-5G"
②wifi設定ファイルを変更します。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo vim.tiny /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
update_config=1
country=JP
network={
ssid="0C8FFree-2G" <==ここにSSIDを記入
psk="55526450646823" <==ここにパスワードを記入
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
}
#↓別のネットワークを設定する時
network={
ssid="0C8FFF327F68-5G" <==ここにSSIDを記入
psk="5512697567952" <==ここにパスワードを記入
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
}
#入力が終了したら、保存して終了。
③RaspberryPiを再起動
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo reboot
④接続確認:「ifconfigコマンド」「pingコマンド」を使用
最後に、設定ができているか、接続できているか確認します。
まず、設定できているかどうかは「ifconfig」コマンドをターミナルに入力しましょう。
wifiだけ表示したい場合は、「ifconfig wlan0」と入力しましょう。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ifconfig
wlan0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 162.168.4.4 netmask 255.255.200.0 broadcast 192.168.3.255
inet6 fe80::8b91:1z1z:6441:4fbb prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether z8:27:zb:z7:z4:68 txqueuelen 1000 (イーサネット)
RX packets 1190 bytes 75076 (73.3 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 487 bytes 92827 (90.6 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
次に、接続ができているかどうか確認します。pingコマンドを入力しましょう。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ping -c 5 162.168.4.4
PING 162.168.4.4 (162.168.4.4) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 162.168.4.4: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.136 ms 64 bytes from 162.168.4.4: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.124 ms 64 bytes from 162.168.4.4: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.098 ms 64 bytes from 162.168.4.4: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.097 ms 64 bytes from 162.168.4.4: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.120 ms --- 162.168.4.4 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 151ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.097/0.115/0.136/0.015 ms
これでwifiの設定はOK。
Ethernetの接続設定
Ethernetを使用して、staticにRaspberryPiを接続したい場合は、設定ファイルを書き換える作業を行います。
設定の流れは、コマンドラインでwifiの設定する時とさほど変わりません。
①「/etc/dhcpcd.conf」の設定ファイルを編集
今回はココを編集します。
まず初期設定時の「/etc/dhcpcd.conf」内容を記載します。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo cat /etc/dhcpcd.conf
# A sample configuration for dhcpcd. # See dhcpcd.conf(5) for details. # Allow users of this group to interact with dhcpcd via the control socket. #controlgroup wheel # Inform the DHCP server of our hostname for DDNS. hostname # Use the hardware address of the interface for the Client ID. clientid # or # Use the same DUID + IAID as set in DHCPv6 for DHCPv4 ClientID as per RFC4361. # Some non-RFC compliant DHCP servers do not reply with this set. # In this case, comment out duid and enable clientid above. #duid # Persist interface configuration when dhcpcd exits. persistent # Rapid commit support. # Safe to enable by default because it requires the equivalent option set # on the server to actually work. option rapid_commit # A list of options to request from the DHCP server. option domain_name_servers, domain_name, domain_search, host_name option classless_static_routes # Respect the network MTU. This is applied to DHCP routes. option interface_mtu # Most distributions have NTP support. #option ntp_servers # A ServerID is required by RFC2131. require dhcp_server_identifier # Generate SLAAC address using the Hardware Address of the interface #slaac hwaddr # OR generate Stable Private IPv6 Addresses based from the DUID slaac private # Example static IP configuration: #interface eth0 <==ここを編集する #static ip_address=192.168.0.10/24 <==ここを編集する #static ip6_address=fd51:42f8:caae:d92e::ff/64 #static routers=192.168.0.1 #static domain_name_servers=192.168.0.1 8.8.8.8 fd51:42f8:caae:d92e::1 # It is possible to fall back to a static IP if DHCP fails: # define static profile #profile static_eth0 #static ip_address=192.168.1.23/24 #static routers=192.168.1.1 #static domain_name_servers=192.168.1.1 # fallback to static profile on eth0 #interface eth0 #fallback static_eth0 SSID 0C8FFree-2G <==wifiの設定が完了しているとここに記載される。 inform 162.168.4.4 SSID 0C8FFree-2G inform 162.168.4.4
編集する場所を以下に示します。
# Example static IP configuration: interface eth0 <==ここの[#]を消す static ip_address=162.168.0.10/24 <==ここの[#]を消す #static ip6_address=zz51:42z8:zzze:d92z::ff/64 #static routers=162.168.4.4 #static domain_name_servers=162.168.4.4.0.1 8.8.8.8 zz51:42z8:zzze:d92z::1
②RaspberryPiを再起動する。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo reboot
③接続確認:「ifconfigコマンド」「pingコマンド」を使用
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ping -c 5 192.168.0.10
接続が確認出来たら、ssh設定をします。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ssh pi@192.168.0.10
pi @192.168.0.10's password :
ここでRaspberryPiセットアップ時に設定したパスワードを入力すると、WindowsやMacPCからRaspberryPiを接続可能になります。
詳しい、SSH接続については以下の記事にまとめたので、ご覧ください。
まとめ
以上がネットワーク設定になります。
次は、SSH接続を背セッティングしましょう。






コメント